Appearance
Lookup
Lookups replace codes and IDs with meaningful values from a lookup table. A lookup must return a single, unique value. When defined in forms, a lookup replaces a standard data entry field with a drop-down list of all possible values.
Base Table
The base table is the table queried by the application. In this example, we'll use the tutorial_emp table.
The screenshot below shows raw data from the tutorial_emp table returned by the SQL Query Builder. This table contains a mgr column, which stores the manager's employee number. Without a lookup, an app user would only see this number, which is not meaningful on its own.
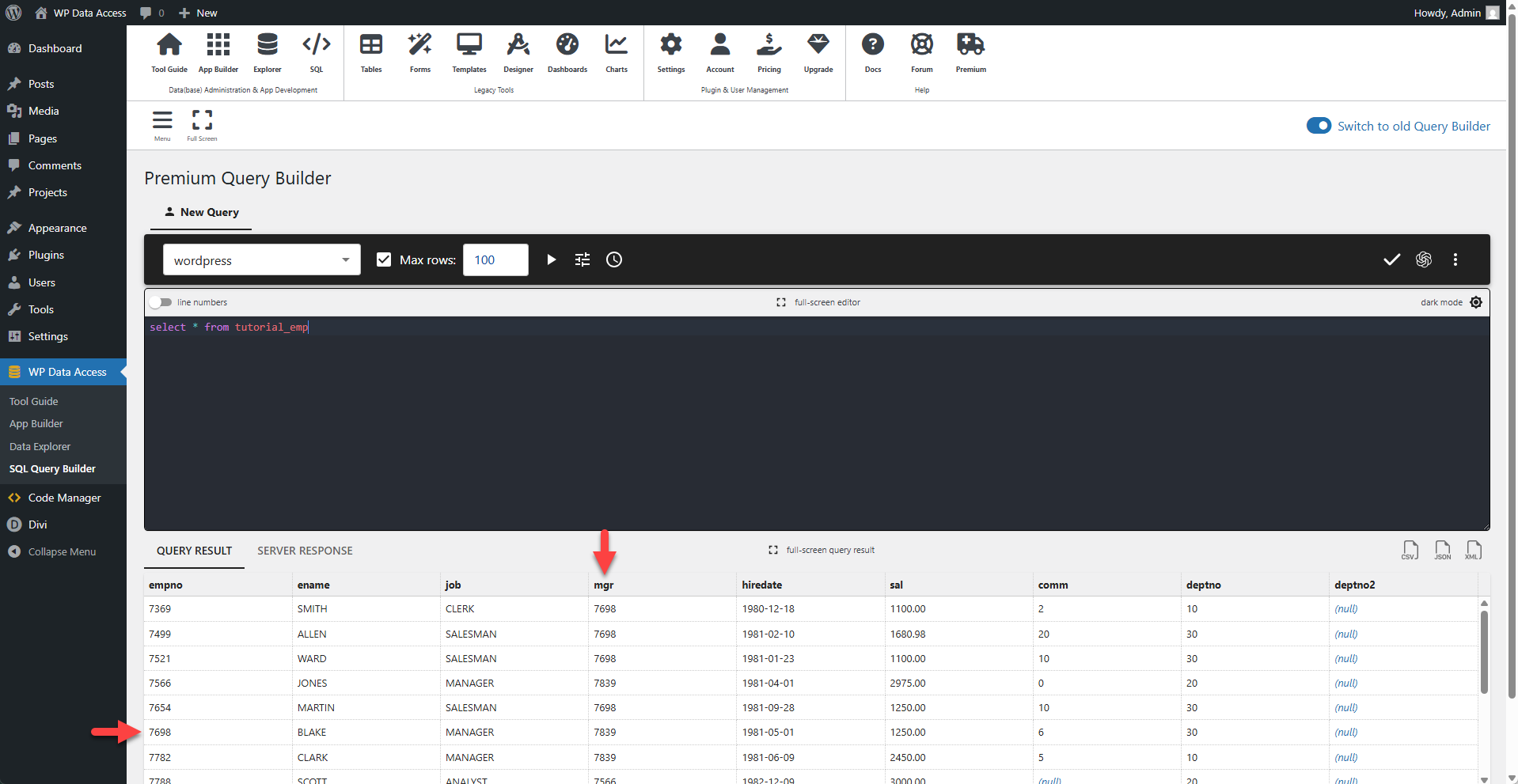
Lookup Table
In this example, the tutorial_emp table also serves as the lookup table. It contains an employee number (empno) and a corresponding employee name (ename) for each employee. The lookup will use this table to replace the manager's employee number with the manager's name.
> A lookup example using different base and lookup tables is available here.
⚙️ Creating Lookups
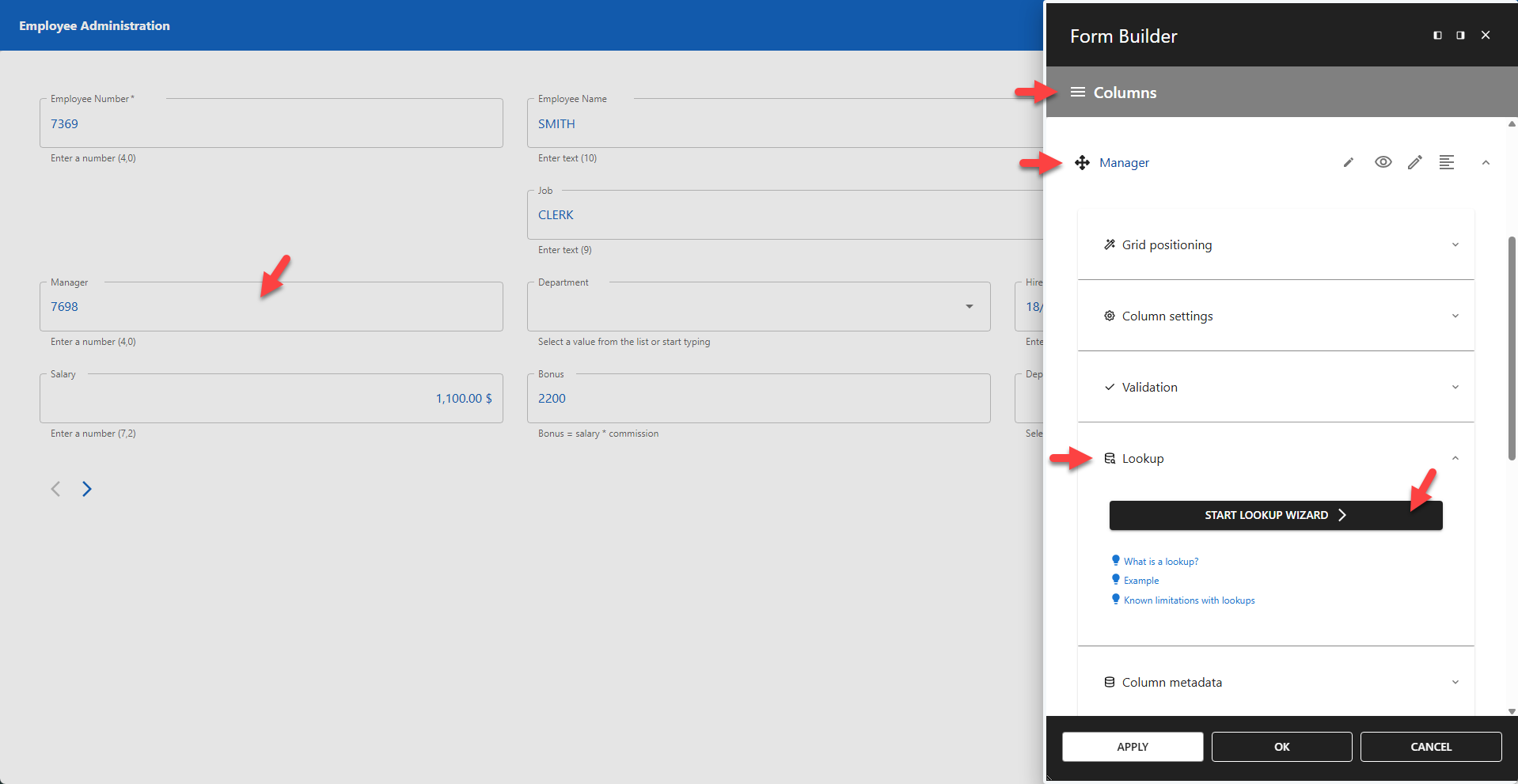
The screenshot below shows the mgr column from the tutorial_emp table. The column label has been changed to Manager. No lookup is defined yet, so the raw employee/manager number is displayed.
Click the START LOOKUP WIZARD button to create a lookup for the mgr column.
1 - Select Database
Select the database where your lookup table is stored.
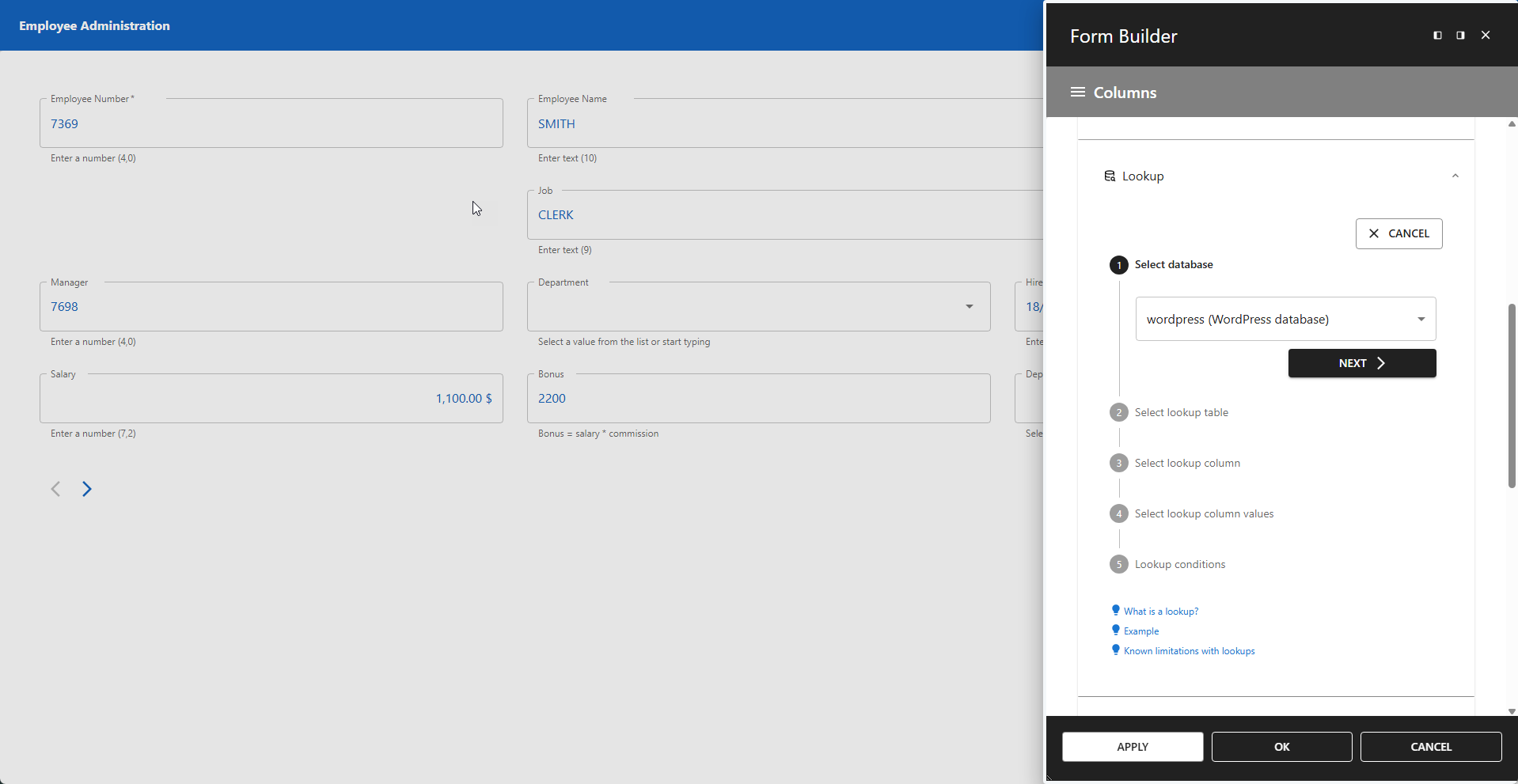
📌 The lookup table does not need to be in the same database as the base table.
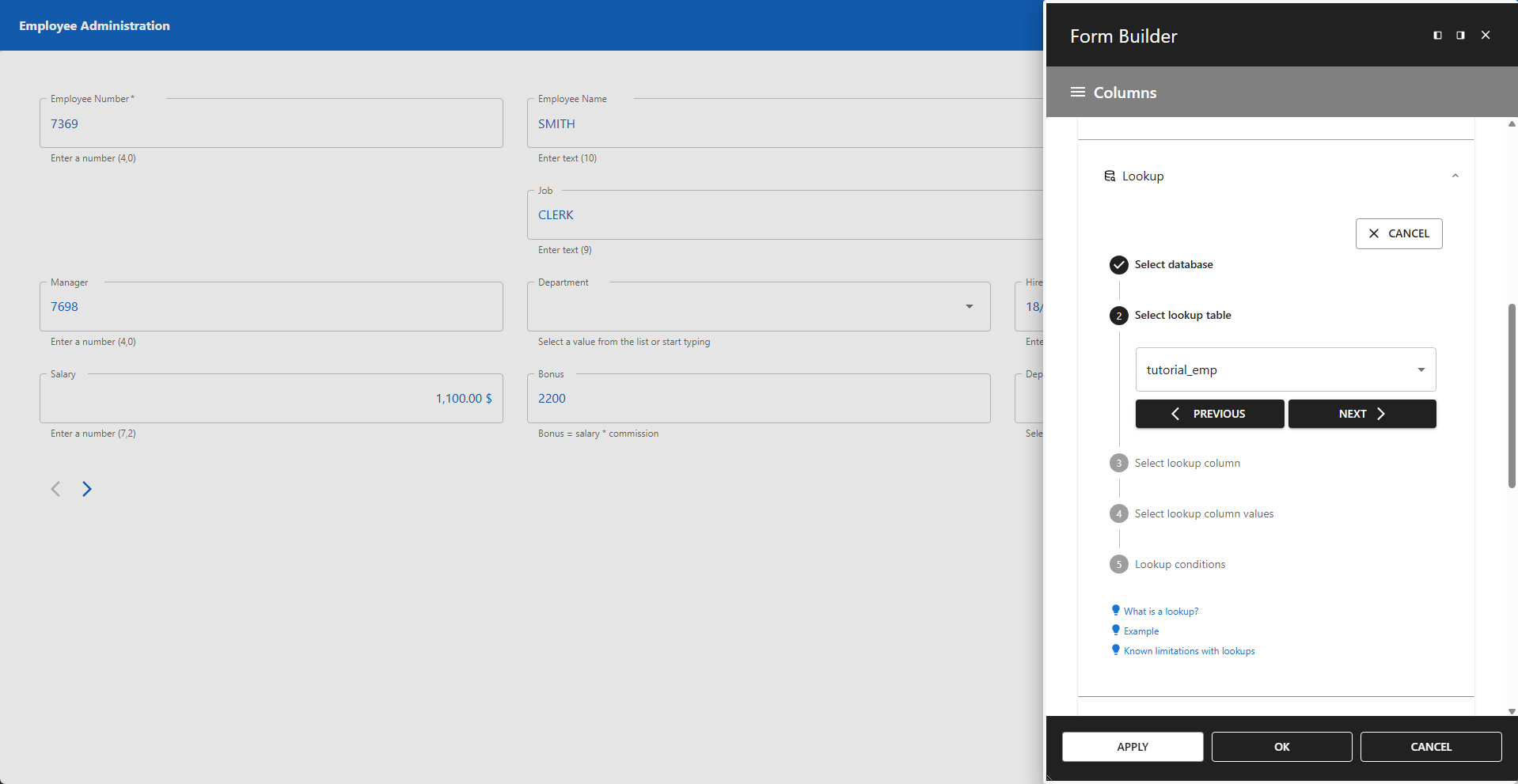
2 - Select Lookup Table
Select the lookup table. In our example, this is the tutorial_emp table.
3 - Select Lookup Column
Select the column in the lookup table that corresponds to the column in the base table you are replacing.
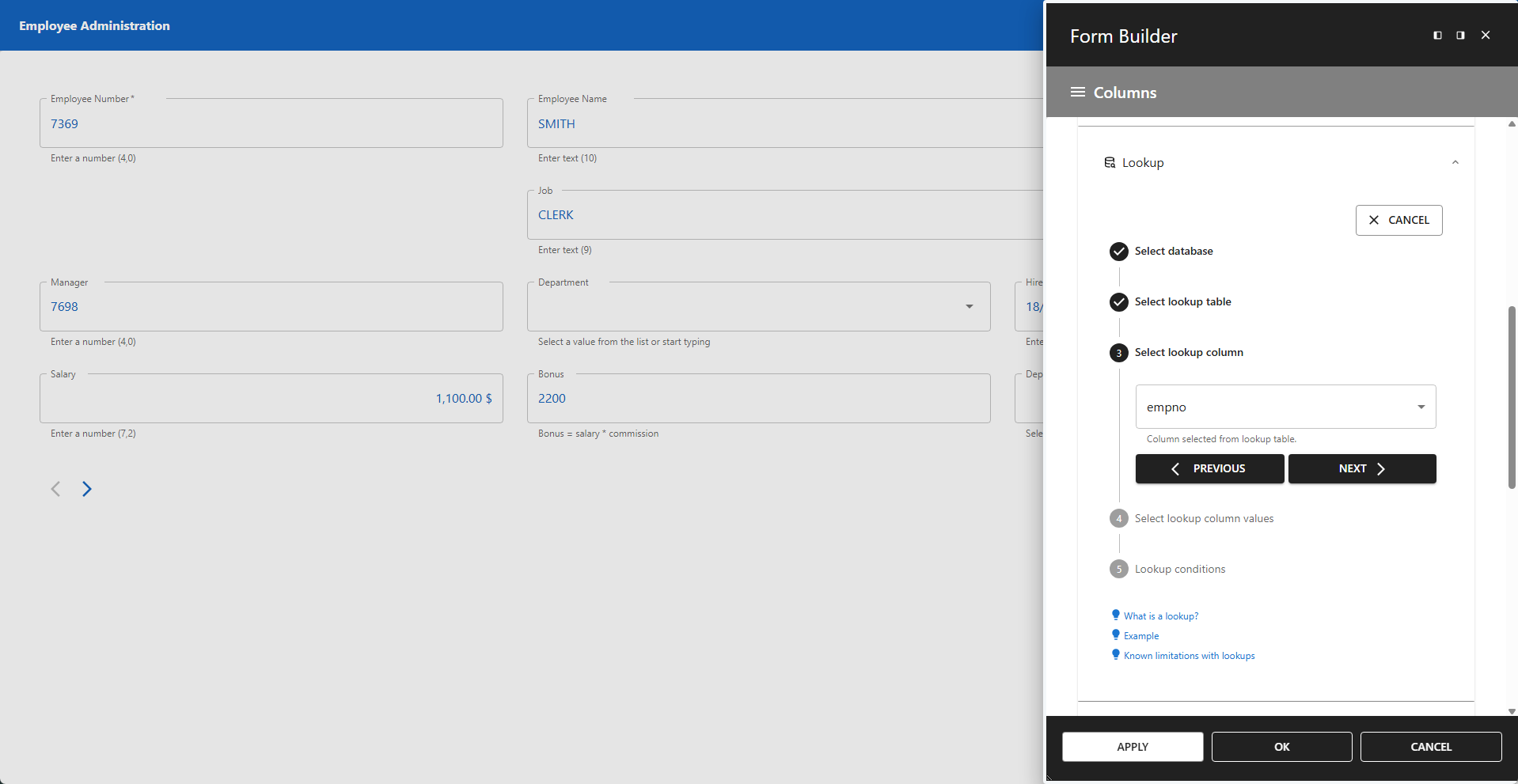
📌 In this example, the empno column from tutorial_emp corresponds to the mgr column from the same table, as a manager is also an employee.
4 - Select Lookup Column Values
Select the column value(s) you want to display. You can choose more than one column. Use the column delimiter field to define a separator between values.
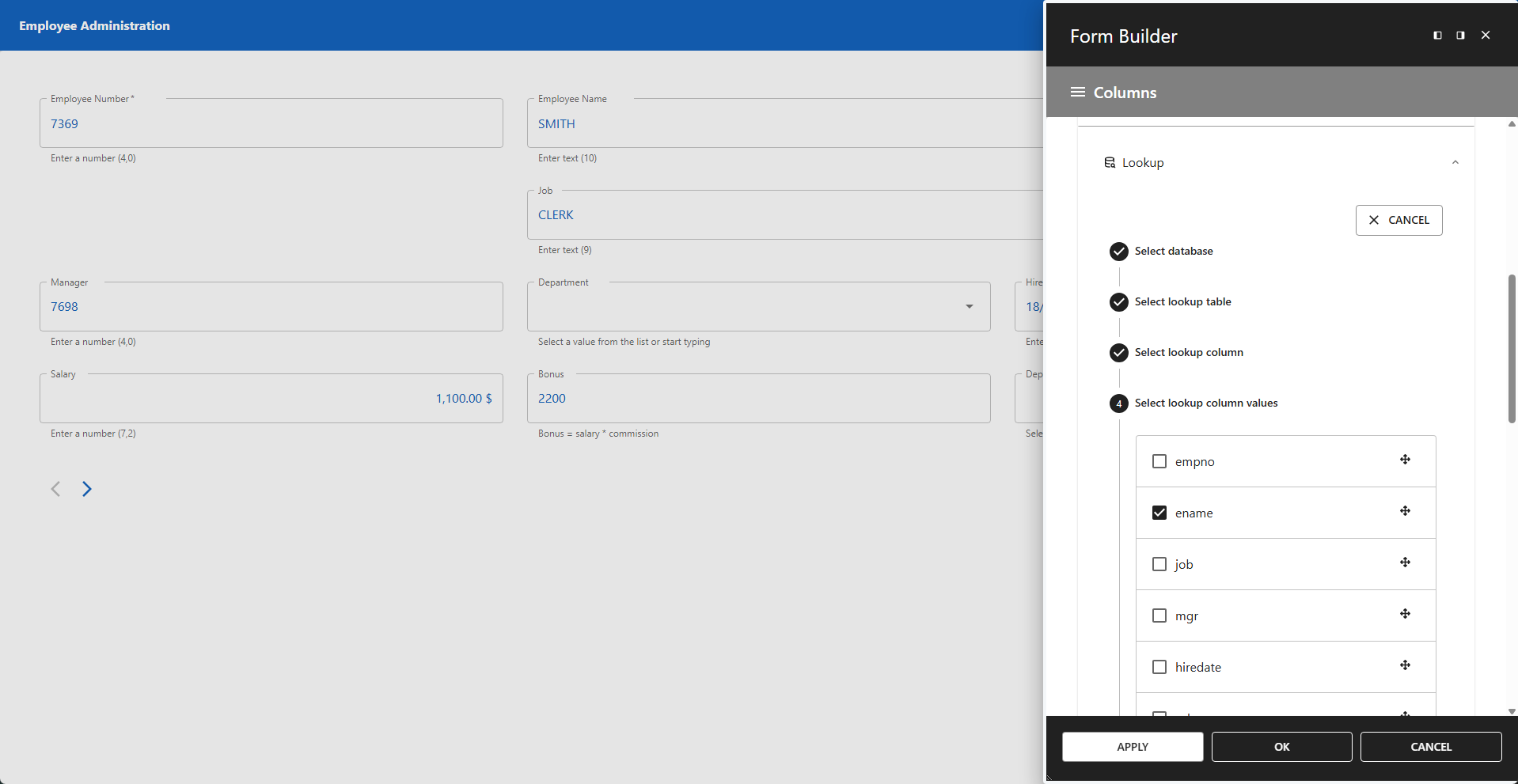
📌 In this example, the ename column is selected, which represents the employee name.
5 - Lookup Conditions
Add any additional conditions to filter the lookup results. This is useful if you store multiple types of lookups in a single table.
5.1 WHERE Clause
You can add a WHERE clause to limit the rows returned.
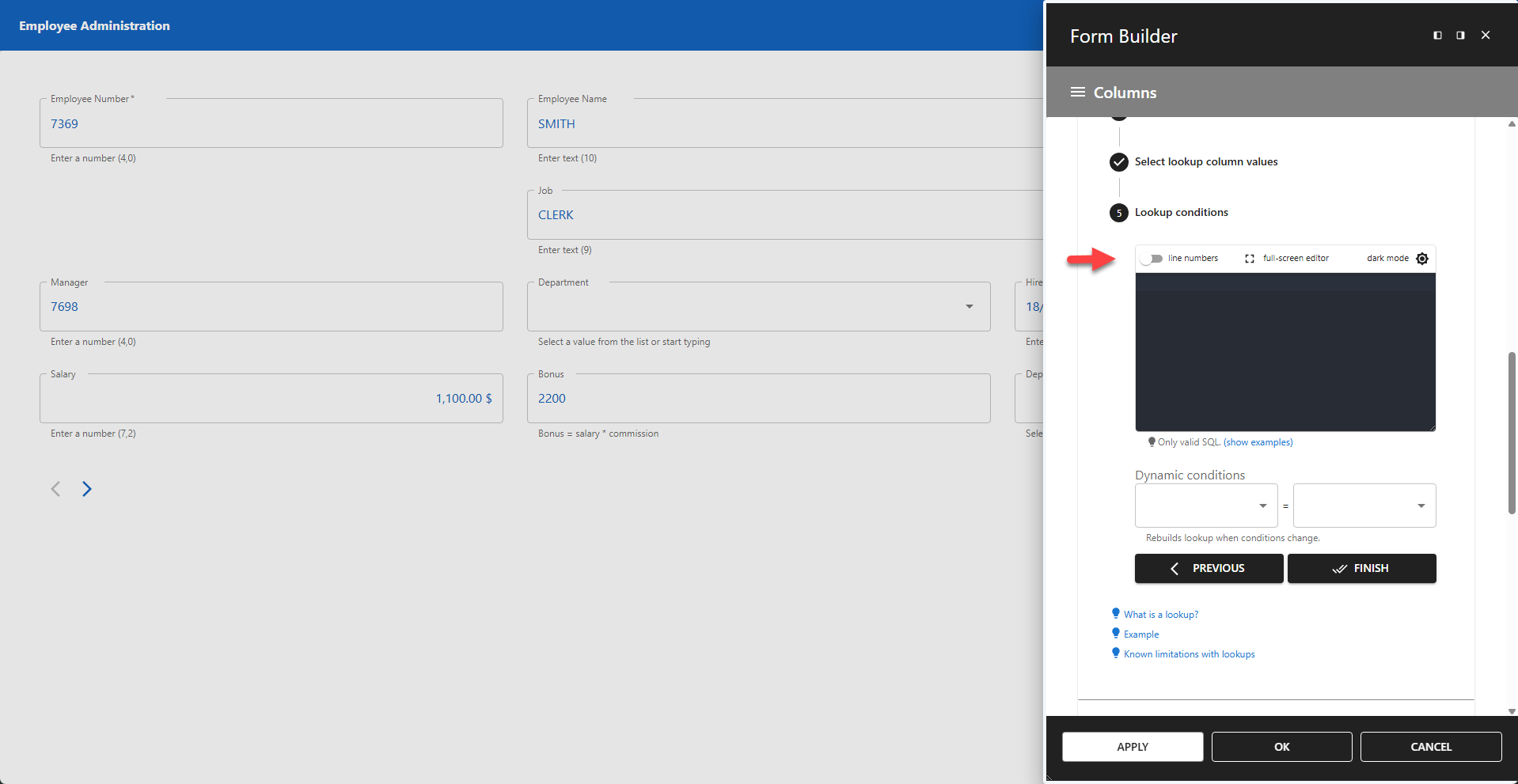
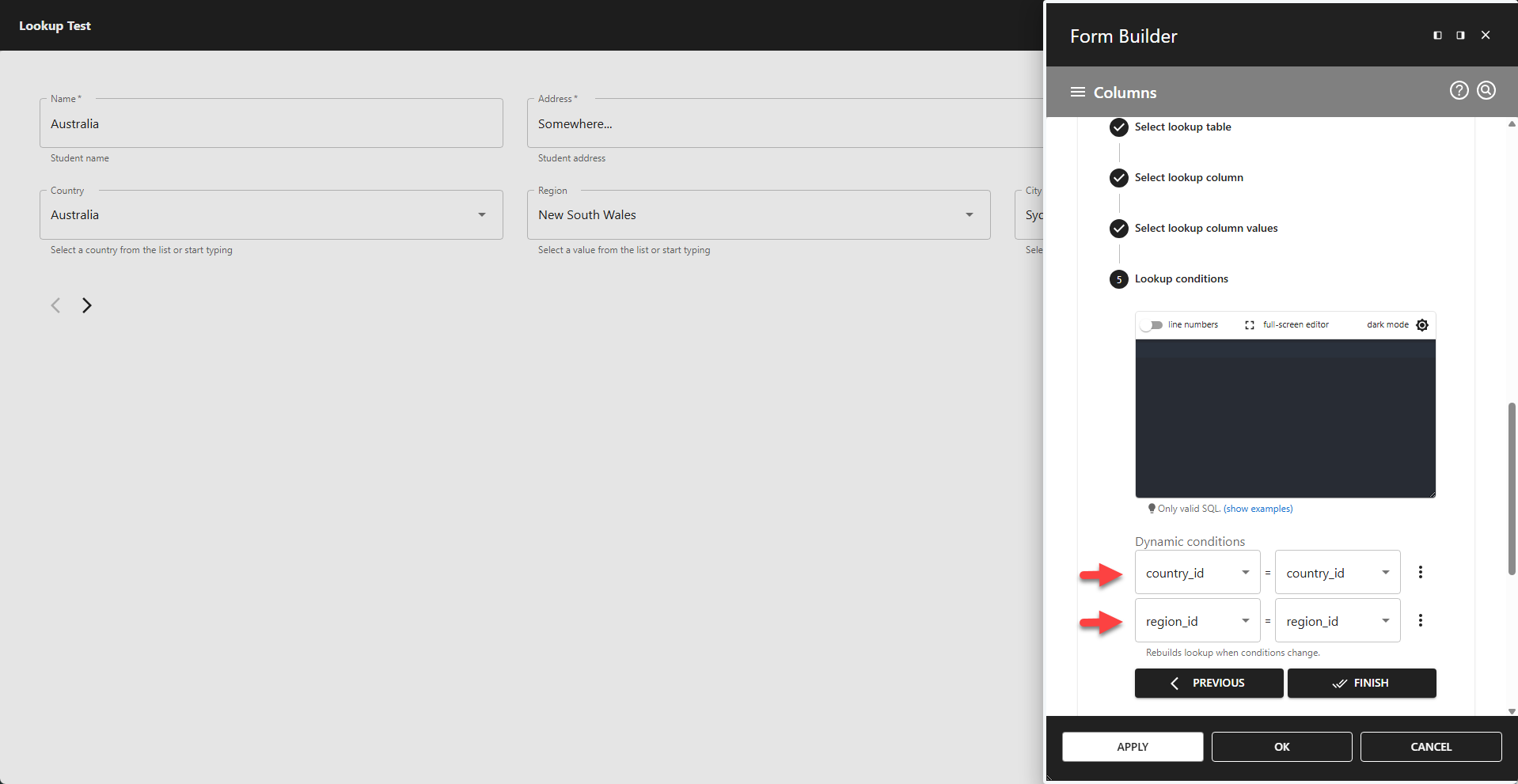
5.2 Dynamic Conditions
Dynamic conditions allow lookups to update interactively based on user input. Each dynamic condition contains two fields:
- The first field references your lookup table.
- The second field references a form field.
When a form field is changed, the corresponding lookup automatically resets, prompting the user to enter a new value. If you have multiple dependent lookups, all of them will reset when a change is made.
✨ Dynamic Conditions Example
Example showing a city lookup that depends on both country and region. If the user changes the country or region, the city field resets.
FINISH
- Click the FINISH button to complete the lookup creation.
- Click APPLY or OK to enable the lookup.
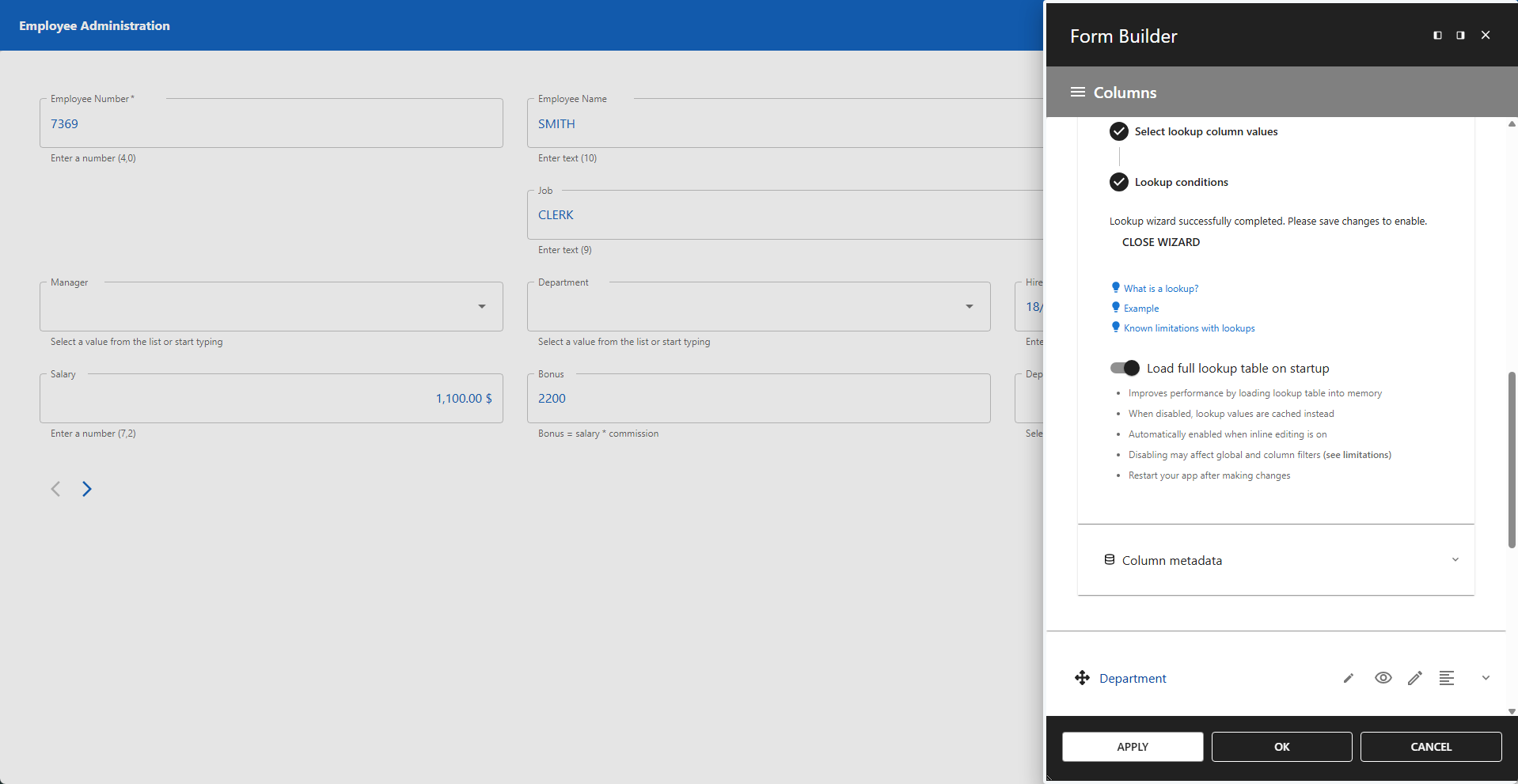
📌 Enable load full lookup table on startup to reduce server load.
📌 Reload your app if the lookup values do not appear immediately.
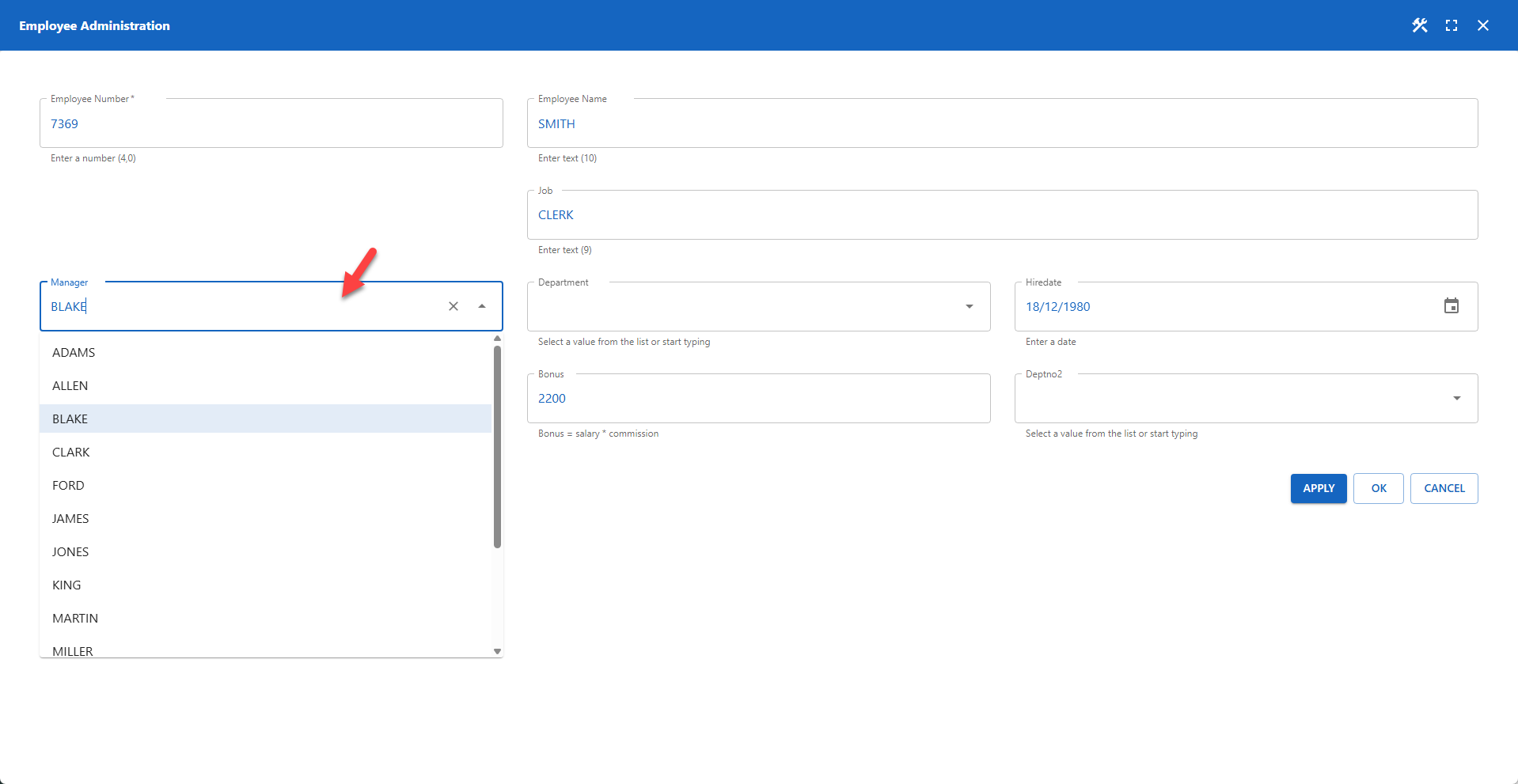
Final Form Layout
The screenshot below shows the result after applying the lookup. The manager field now contains a drop-down list with all allowed values for this column.